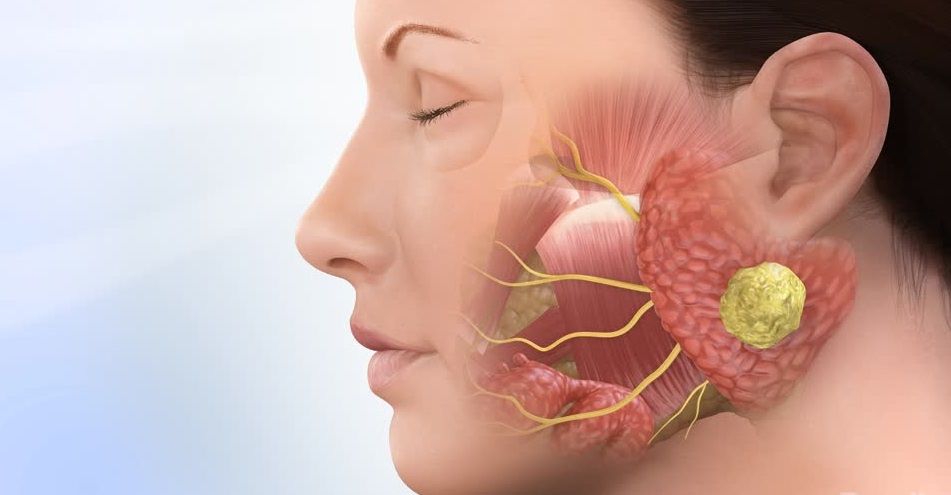
Jaw Cyst and Tumor Surgery
At Tayfun Civak Dental Clinic, we are committed to providing comprehensive care for various dental conditions, including jaw cysts and tumors. Understanding the nature of these issues and the surgical procedures involved can help alleviate concerns and ensure a smooth treatment process. Here’s an overview of jaw cyst and tumor surgery.
What are Jaw Cysts and Tumors?
Jaw Cysts: A jaw cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops within the jawbone or surrounding tissues. Common types include dentigerous cysts, which are associated with unerupted teeth, and radicular cysts, which typically arise from the roots of non-vital teeth.
Jaw Tumors: Jaw tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and may originate from the jawbone or soft tissues. Benign tumors include ameloblastomas and odontogenic tumors, while malignant tumors can involve more serious conditions such as oral cancer.
Why is Surgery Necessary?
Surgery is often required to address jaw cysts and tumors for several reasons:
- Symptom Relief: Cysts and tumors can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort, which surgical removal can alleviate.
- Preventing Complications: Untreated cysts and tumors may lead to further complications, including bone loss, damage to adjacent teeth, or, in the case of malignant tumors, the spread of cancer.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Surgical removal allows for accurate diagnosis through biopsy and enables appropriate treatment planning based on the type and extent of the cyst or tumor.
The Surgical Procedure
Diagnosis and Planning: The first step involves a thorough examination, including imaging studies such as X-rays or CT scans, to determine the size, location, and nature of the cyst or tumor. A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Anesthesia: To ensure a pain-free experience, local anesthesia is used to numb the surgical area. In some cases, sedation or general anesthesia may be recommended based on the complexity of the procedure.
Surgical Removal: The procedure involves making an incision in the gum or oral cavity to access the cyst or tumor. The affected tissue is carefully removed, and the area is cleaned and closed with stitches.
Post-Operative Care: After surgery, it is essential to follow care instructions to promote healing and prevent complications. This may include managing pain with medications, maintaining oral hygiene, and adhering to a soft food diet.
Aftercare and Follow-Up
- Wound Care: Follow instructions for wound care to avoid infection and support healing. This includes gentle oral hygiene practices and avoiding trauma to the surgical site.
- Diet and Activity: Stick to a diet of soft foods and avoid strenuous activities that could impact the healing process.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, evaluate the success of the surgery, and ensure that any necessary further treatment is addressed.
